Net metering is a game-changer in India’s solar energy landscape. It’s a billing system that allows solar power system owners to harness the sun’s energy and receive credits for excess electricity they generate and feed back into the grid. This setup is particularly advantageous for rooftop solar installations, which often produce more energy than the property consumes. Here’s how net metering works in India:
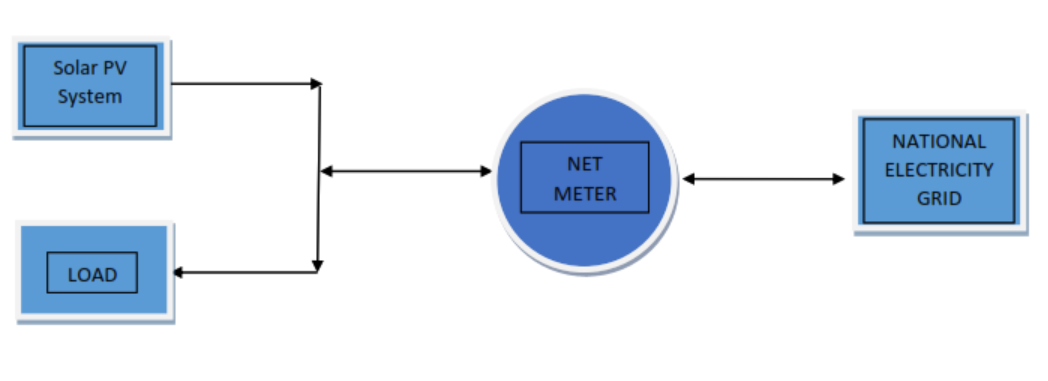
- Solar Panel Installation: To get started, property owners or consumers install solar panels on their rooftops or properties.
- Bi-Directional Meter Installation: Electricity distribution companies (DISCOMs) install bi-directional meters to monitor electricity flow in two directions – from the grid to the property and vice versa.
- Efficient Energy Use: During the day, solar panels generate electricity, primarily fulfilling the property’s energy needs. If there’s surplus electricity generated, it flows back into the grid, with the bi-directional meter tracking this flow.
- Billing with Credits: At the end of the billing cycle, consumers are billed based on their net electricity consumption. If the property generates more electricity than it consumes, surplus units are credited to the consumer’s account, offsetting future bills.
Latest Solar Power Plant Installation Policies in India: Stay Informed
India is committed to harnessing the power of the sun through evolving policies and incentives. These policies aim to boost solar power plant installations, reduce carbon emissions, and enhance energy security. Here are some key features of the latest solar power installation policies:
- Financial Incentives: Government entities at both central and state levels often provide subsidies and incentives to promote solar power plants. These may include capital subsidies, tax benefits, and reduced import duties on solar equipment.
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): Consumers can opt for power purchase agreements, allowing them to install solar power plants without the initial capital investment. Through PPAs, consumers buy solar power at predetermined rates.
- Net Metering and Feed-in Tariffs: Many states embrace net metering for rooftop solar installations, ensuring consumers receive credit for surplus electricity. Larger solar power plants may also benefit from feed-in tariffs, guaranteeing fixed prices for the electricity generated.
- Renewable Purchase Obligations (RPOs): Government mandates require a specific percentage of total energy consumption to come from renewable sources, including solar. Compliance with RPOs encourages solar power adoption.
- Solar Parks: India is fostering the development of solar parks with essential infrastructure and clearances. These parks attract investments and simplify the setup of solar power projects.
Please note that solar energy policies and incentives can differ from state to state. To ensure you have the most current information on solar power regulations and incentives in your area, consult local authorities or seek guidance from solar energy experts.
